Diabetes is a serious medical condition that affects millions of people. Living with diabetes requires an awareness to maintain. In this blog, we will explore all about diabetes, from recognizing signs & symptoms to understanding its causes, risk factors and how it’s diagnosed.
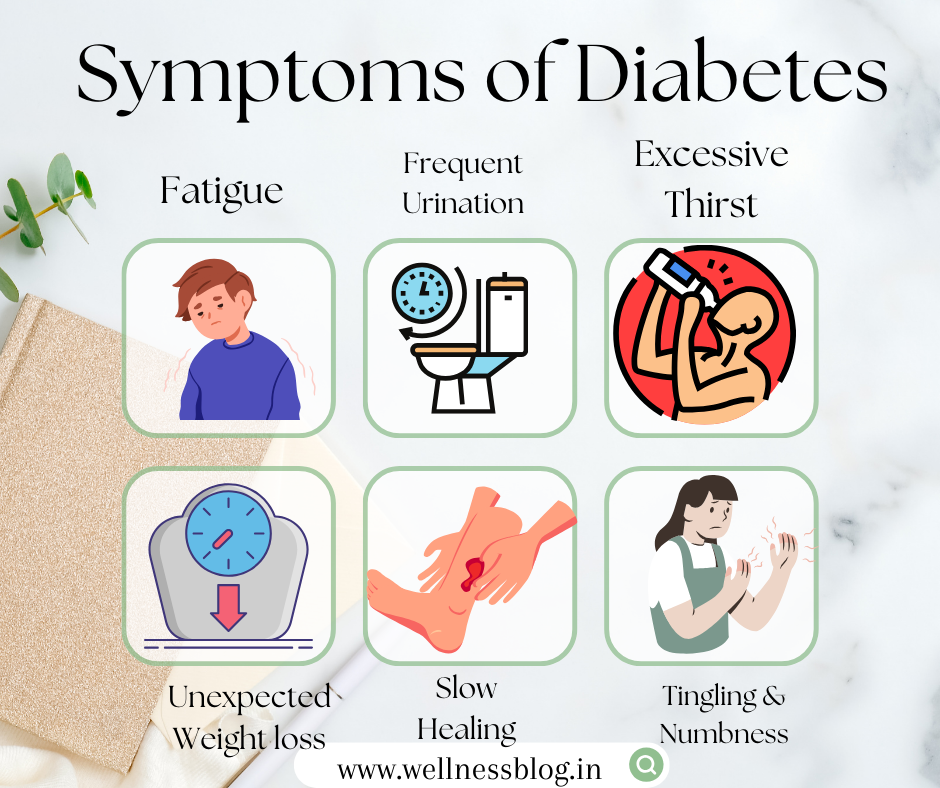
Symptoms of Diabetes:
The symptoms of diabetes can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Common symptoms of Diabetes include:
1. Excessive Thirst and Hunger:
- Feeling thirsty all the time and experiencing unexplained hunger are common early signs.
2. Frequent Urination:
- If you find yourself making more trips to the bathroom, especially at night, it might be a red flag.
3. Fatigue and weakness:
- Feeling unusually tired, even after a good night’s sleep, could be a symptom of diabetes.
4. Unexplained Weight Loss:
- Shedding pounds without trying? It’s another potential sign to pay attention to.
5. Slow healing of wounds:
- Delayed or longer healing from cuts and bruises may be a sign of uncontrolled diabetes.
6. Blurred vision:
- Sudden increase of blood sugar levels can damage the eye lens, resulting in blurred vision.
7. Tingling and numbness in the hands and feet:
- Induced nerve damage, known as diabetic neuropathy can cause tingling and numbness in the hands and feet.
If you experience any of these symptoms it is essential to consult a doctor for proper evaluation and treatment.
Causes of Diabetes:
Diabetes develops when the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin (Type 1 diabetes) or becomes resistant to insulin (Type 2 diabetes). The exact causes of diabetes are complex and can involve genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors.
Risk Factors of Diabetes:
Several factors can increase the risk of developing diabetes, including:
1. Family History:
- If your close relatives or parents have diabetes, your risk may be higher.
2. Age:
- The risk increases with age, especially after 45.
3. Lifestyle:
- Lack of physical activity, poor diet, and excess weight can increase the risk.
4. High Blood Pressure
- Patients with high Blood pressure are more prone to diabetes than others.
It’s essential to be aware of these risk factors and take proactive steps to manage them to reduce the risk of developing diabetes.
Diagnosis of Diabetes:
Diabetes is diagnosed through various tests that measure blood sugar levels. Common diagnostic tests include:
1. Blood Tests:
- Fasting plasma glucose test is the most common method used to diagnose diabetes. This measures blood sugar levels after fasting overnight.
2. Hemoglobin A1c test:
- Provides an average of blood sugar levels over the past two to three months.
3. Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT):
- A more comprehensive test to measure how your body handles glucose.
4. Symptoms and Physical Exam:
- Your doctor will consider your symptoms and may perform a physical examination.
5. Risk Assessment:
- Understanding your risk factors helps guide the diagnostic process.
Conclusion:
Being aware of the symptoms, causes, risk factors, and the diagnostic process is crucial for early intervention and effective management. If you suspect diabetes or have concerns, don’t hesitate to consult with a diabetologist. Remember, knowledge helps you to take control of your health journey. Stay informed, stay healthy!

